DUBs Family
Protein ubiqutinylation, the covalent post-translational addition of ubiquitin, and deubiquitinylation is a dynamic and reversible process, orchestrated by the concerted effort of the ubiquitin ligase and deubiquitin peptidase (DUBs) families. Ubiquitinylation is critical in regulating protein degradation, protein-protein interactions, cellular localization, and enzymatic activity - dictating numerous important cellular processes.
DUBs are a family of peptidases responsible for cleaving or editing these ubiquitin chains, thereby rescuing proteins from proteosomal degradation and restoring intracellular signaling cascades. With 6 distinct classes of DUBs, over 100 diverse family members total, categorized by their well characterized catalytic domains, DUBs serve as attractive therapeutic targets. Dysregulation of DUB activity has been implicated in a variety of human disease states, most commonly cancer. Recent advancements have contributed to the renewed interest in the therapeutic potential of pharmacologically modulating DUBs.
The Biortus Protein Catalogue currently offers 67 DUBs expressed in multiple expression systems, with 3 structurally resolved and specific in-house biochemical assays for all 6 classes of DUBs readily available.
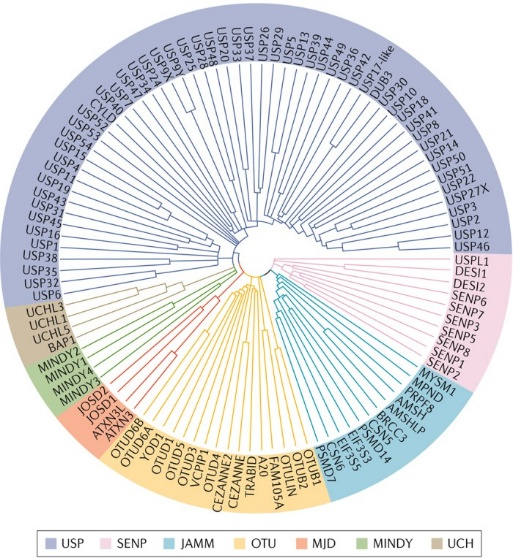
Figure 1. DUB and Setrin/SUMO specific protease (SENP) phylogenetic tree. All 6 classes of DUBs are represented here: ubiquitin-specific proteases (USP), ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolases (UCH), Machado-Josephin domain-containing proteases (MJD), ovarian tumor proteases (OTU), motif-interacting with ubiquitin-containing novel DUB family (MINDY) and JAB1, MPN, MOV34 family (JAMM).
from Harrigan, J. et al, Nature Reviews 2016.

 Drug Targets
Drug Targets 
