Biortus Delivering ABCB10 Protein and Cryo-EM Structures
Release Time:
2022-04-26 09:46
Source:
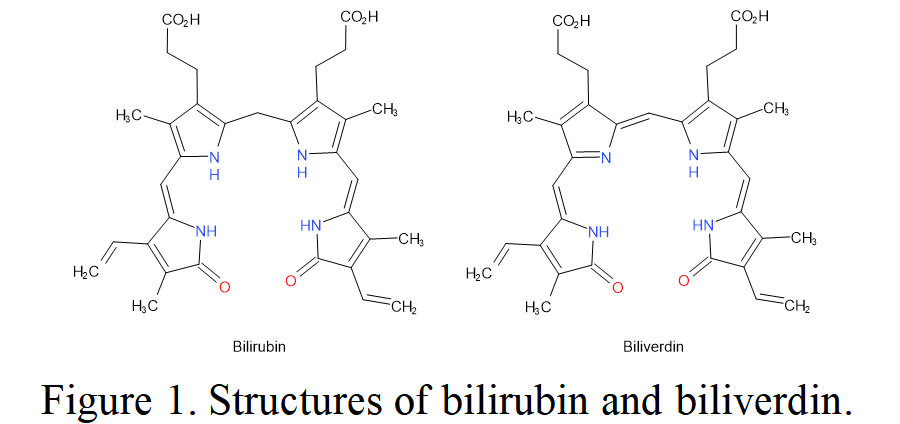
A member of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter family located in the inner membrane of mitochondria, ABCB10 in the liver functions as a transporter of liver biliverdin, the reduction product of bilirubin (Fig. 1).
A large body of evidence suggested that dysregulated activity of ABCB10 led to high level of bilirubin in human liver, causing liver diseases including fatty liver disease. Blocking ABCB10 function in liver cells protected obese mice from hyperglycemia and fatty liver disease [1], demonstrating ABCB10 a potential drug target for therapeutic treatment of hyperglycemia and fatty liver disease.
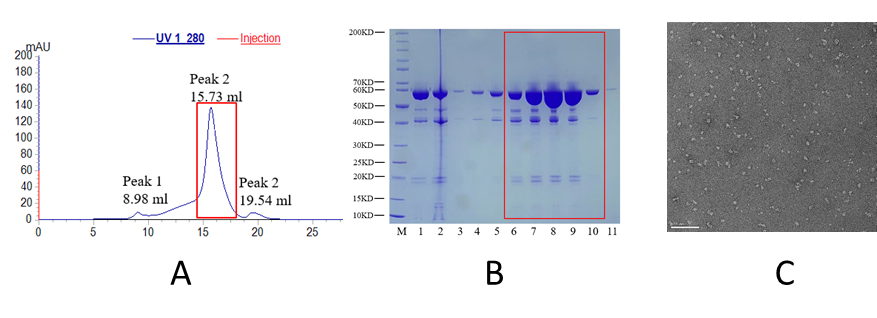
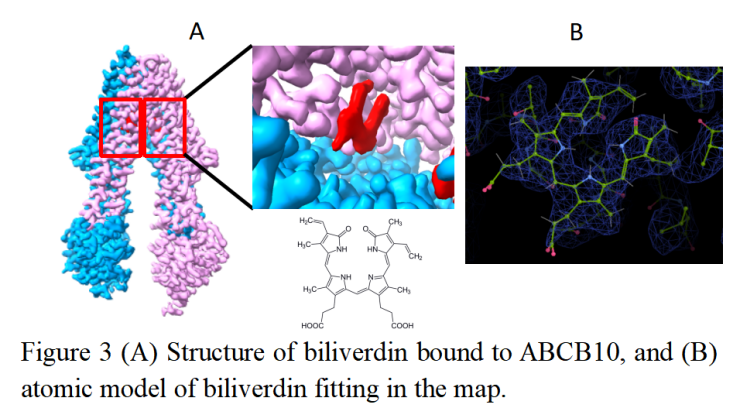
As part of TransporterSuite® Campaign effort, Biortus’s team has established a robust ABCB10 expression and purification process, and delivered large quantity of pure and stable ABCB10 protein sample for activity profiling and structural biology studies (Fig. 2). Taking advantage of its state-of-the-art cryo-EM facility, Biortus’s cryo-EM team has solved both apo- and biliverdin-bound ABCB10 structures to near-atomic resolution (Fig.3). The complete package of protein to assay to structure on ABCB10 prepared by Biortus’s team presents a powerful toolbox for SBDD on ABCB10.
[1] Shum, Michael, et al. "ABCB10 exports mitochondrial biliverdin, driving metabolic maladaptation in obesity." Science translational medicine 13.594 (2021): eabd1869.

